Feb 11,2026
NextAs electric micro vehicles continue to gain popularity across Europe—particularly in the L6e-BP electric quadricycle segment—motor selection has become a key factor influencing efficiency, drivability, and overall system design.
Among the most widely used motor technologies in compact electric vehicles are Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSM) and AC induction motors. While both solutions are technically mature and suitable for L6e applications, their differences in efficiency, torque characteristics, packaging, and cost structure can significantly affect real-world urban driving performance.
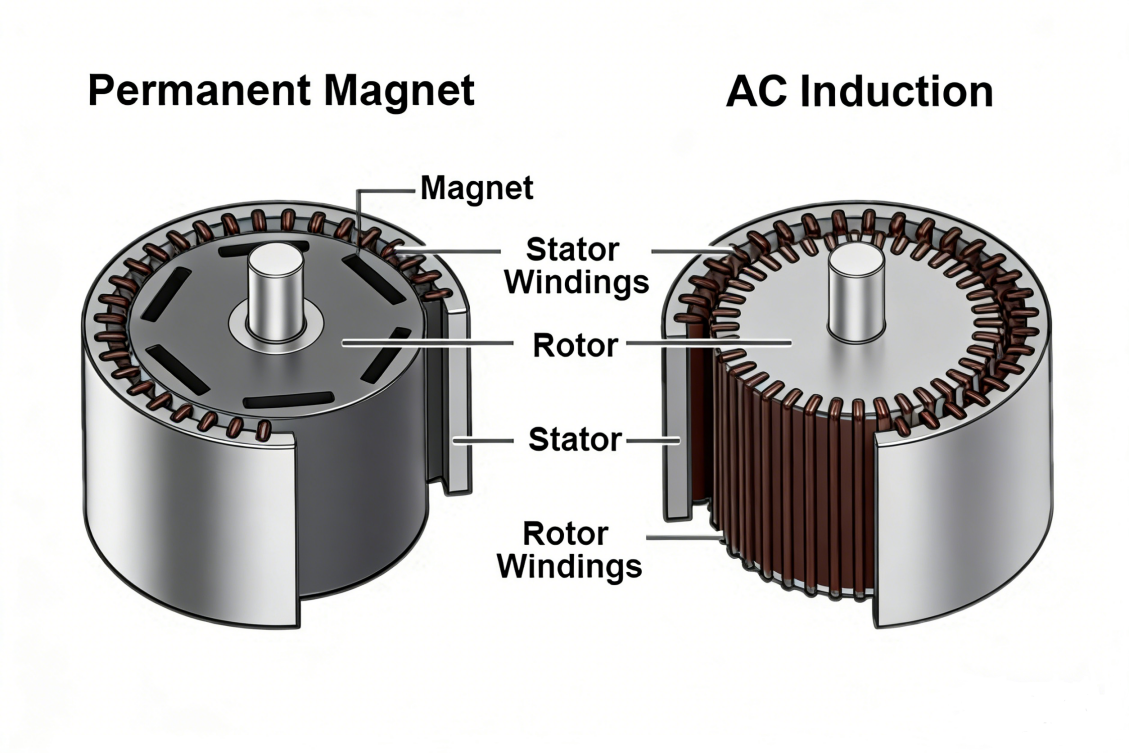
The fundamental difference between PMSM and AC induction motors lies in how torque is generated and how efficiently electrical energy is converted into mechanical output in electric vehicles.
⭐ PMSM motors use permanent magnets in the rotor, allowing the motor to operate synchronously with the magnetic field. This typically results in higher efficiency, particularly at low and medium speeds.
⭐ AC induction motors generate torque through electromagnetic induction, which involves rotor current losses and generally leads to slightly lower efficiency under partial load.
In urban driving conditions where micro vehicles operate at relatively low speeds and frequent stop-and-go cycles, efficiency differences can influence overall energy consumption.
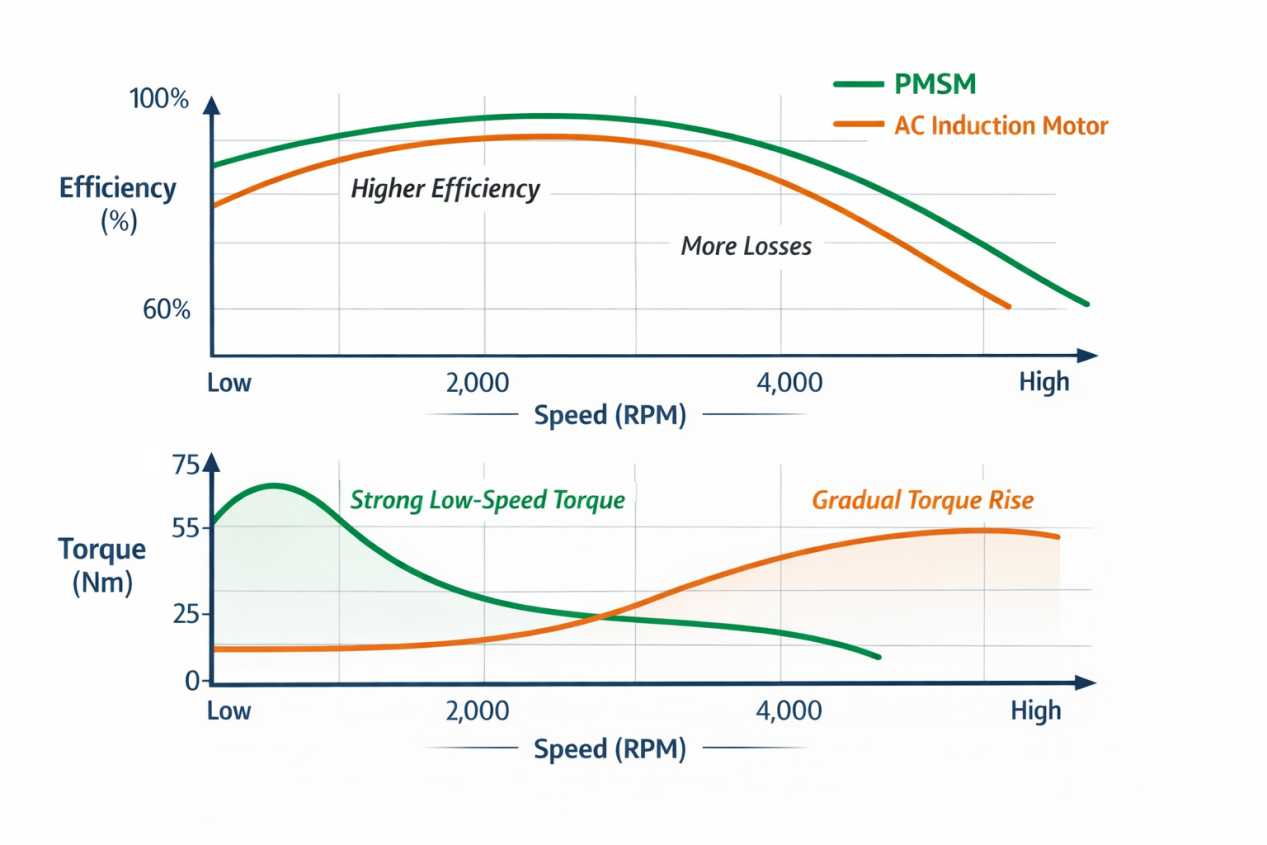
Motor torque delivery affects drivability, especially in city environments.
⭐ PMSM motors are known for smooth and responsive low-speed torque, which can improve acceleration control and hill-start performance.
⭐ AC induction motors tend to deliver torque in a more gradual manner and may require higher current to achieve similar low-speed response.
Both motor types are capable of meeting the performance requirements of L6e vehicles, though their torque characteristics differ slightly depending on control strategy and tuning.

Packaging efficiency is a key consideration in compact electric vehicles.
⭐ PMSM motors are generally more compact and lighter for the same power output.
⭐ AC induction motors often require a larger motor volume and additional current to reach equivalent performance levels.
These differences can affect overall vehicle layout, weight distribution, and available space for batteries or other components.
From a durability standpoint, both motor technologies are well established.
⭐ AC induction motors have a long history in industrial applications and are valued for their mechanical simplicity and robustness.
⭐ PMSM motors, while relying on permanent magnets, benefit from reduced rotor losses and lower heat generation, which can support long-term efficiency.
Actual reliability depends heavily on system design, cooling strategy, and motor control electronics rather than motor type alone.
Cost structures vary between the two technologies.
⭐ AC induction motors avoid the use of rare-earth magnets, which can reduce exposure to material price fluctuations.
⭐ PMSM motors require permanent magnets, which may influence cost and sourcing but also contribute to higher efficiency and compact design.

The ELFGOGO E6 adopts a Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor, reflecting a design focus on efficiency, compact packaging, and smooth low-speed drivability—characteristics that align well with typical European urban micro-mobility use cases.
At the same time, both PMSM and AC induction motors remain technically viable solutions within the L6e segment, and the optimal choice ultimately depends on vehicle positioning, operating environment, and target customer priorities.